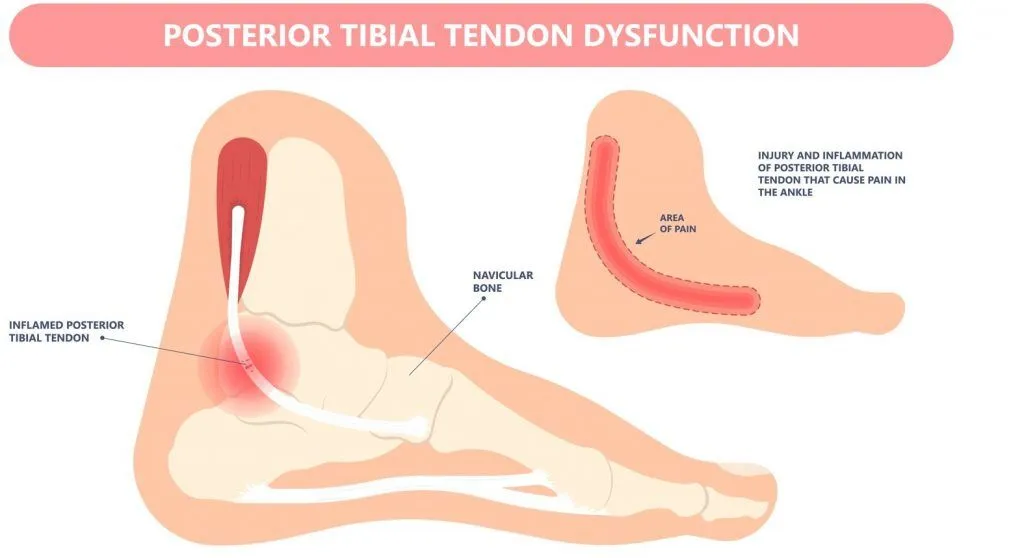
What Is Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
If you’ve been feeling a sharp, pulling ache along the inside of your ankle, especially after a long day of walking, you might be dealing with more than just tired legs. You tried to ignore it, but the achy feeling in your ankle keeps haunting you when you’re shopping along Orchard Road or after exercising. If this sounds like your symptoms, you could be having posterior tibial tendonitis – an inflammation of a key tendon that supports your arch and helps you push off.
Posterior tibial tendonitis is one of the most common chronic conditions causing medial ankle pain, particularly in Singapore and other Asian countries. This condition is often due to a recent sharp rise in your daily step count, or after an intense sport session, such as HIIT or Muay Thai. Most people will dismiss this as just tired legs and pay little attention to it. Over time, the pain creeps up gradually and later makes everyday activities — from walking to climbing stairs — uncomfortable.
Importantly, when left untreated, posterior tibial tendonitis can change your foot shape progressively, leading to an adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. If you look around at some of our older people’s feet, you might see some of them struggling to walk because they’ve reached the late stage of the deformity.
Functions Of The Posterior Tibial Tendon
The posterior tibial tendon runs along the inside of your ankle and attaches to the navicular bone in the foot. When the tendon contracts, it helps lift your foot arch and your heel off the ground, making your foot a stable lever and allowing you to propel forward effectively.
When there is too much load or stress on the tendon, it becomes inflamed or irritated. In severe cases, the tendon becomes weakened or even torn, leading to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). Without a healthy functioning posterior tibial tendon, your arch will then collapse, and your foot will lose its stability when you walk. That’s why recognising and addressing the condition early is so important.
Need Help? See A Podiatrist Today
Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
At the start, most people will just feel a pulling ache along the inside of the ankle after long periods of walking or exercise. However, as the condition advances, you will notice that the time or distance needed to trigger the pain becomes shorter.
Besides pain after walking or other activities, most people also find that taking the first step after rest is quite painful. As such, some patients will mistakenly assume that they have plantar fasciitis instead. However, the reason for the first-step pain is that, at rest, the tendon is not under tension. As soon as you stand up, the sudden tendon traction will flare the pain instantly.
Generally, the symptoms of posterior tibial tendonitis come “on and off” in the early stages, making it easy for most people to dismiss them. However, once the tendon damage starts to worsen, the other significant symptoms will appear:
- Pain and swelling along the inside of the ankle or arch.
- Pain when taking every step, especially during push-off.
- Difficulty balancing on the affected foot.
- Difficulty standing on tiptoe with the affected foot.
- Gradual flattening of the arch or asymmetrical foot posture of both feet.

Causes and Risk Factors
Like every other tendon in our body, the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed when subjected to sudden, high stress or repeated strain. For most of the time, there isn’t just one single reason for developing posterior tibial tendonitis. Instead, it’s often linked to a combination of lifestyle and physical factors.
What increases load on the posterior tibial tendon?
- Frequent high-impact activities that involve running or jumping, such as HIIT or basketball.
- Sudden rise in step count or prolonged walking, such as during a recent overseas holiday.
- Wearing minimalistic footwear (e.g. ballet flats, barefoot shoes) or shoes that are worn out.
- Tight calf muscles, which cause your foot to compensate by pronating more
- Leg length difference, which causes one foot to pronate more.
Who carries a higher baselink risk?
- Age between 40 to 60, especially ladies after menopause.
- Higher BMI.
- Sudden weight gain due to pregnancy.
- Jobs that require long hours of standing.
- Persons with flat feet, which will place more strain on the posterior tibial tendon.
- Persons with congenital bony deformities, such as having an os navicular bone
Managing Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Understanding the possible causes and risk factors helps guide the management plan. Fortunately, most early cases will respond well to conservative measures. And when it comes to posterior tibial tendonitis treatment, the first thing you should do is to reduce the stress on the tendon. Reducing stress gives your tendon the right opportunity to recover. We generally do not recommend over-relying on taking anti-inflammatories, as you are just masking the pain without addressing the underlying cause of the problem. Ultimately, the right treatment plan will depend on how advanced your condition is, which your podiatrist should first determine.
For mild, early cases, you can start by taking steps to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Avoid or reduce high-impact sports or long hours of standing to reduce strain on the tendon.
- Apply the RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) technique to help control swelling.
- Anti-inflammatories, if prescribed, should not be taken for more than 2 weeks in a row.
- Avoid slippers or barefoot shoes and switch to proper, supportive, and stable sport shoes.
For cases that have been persistent for 2 to 3 months or are not responding to early measures, podiatric intervention and rehabilitation are necessary.
- Custom orthotics can be designed to help realign the foot, support and reduce stress on the posterior tibial tendon.
- Physical therapy or a structured rehabilitation programme can help strengthen the posterior tibial tendon and the surrounding muscles.
For severe cases with significant flat foot deformity or tendon damage, you should consider advanced treatment to help the tendon heal.
- Advanced therapies such as extracorporeal magnetotransduction therapy (EMTT) and focused shockwave therapy (ESWT) can help signal the body’s natural response and trigger healing processes.
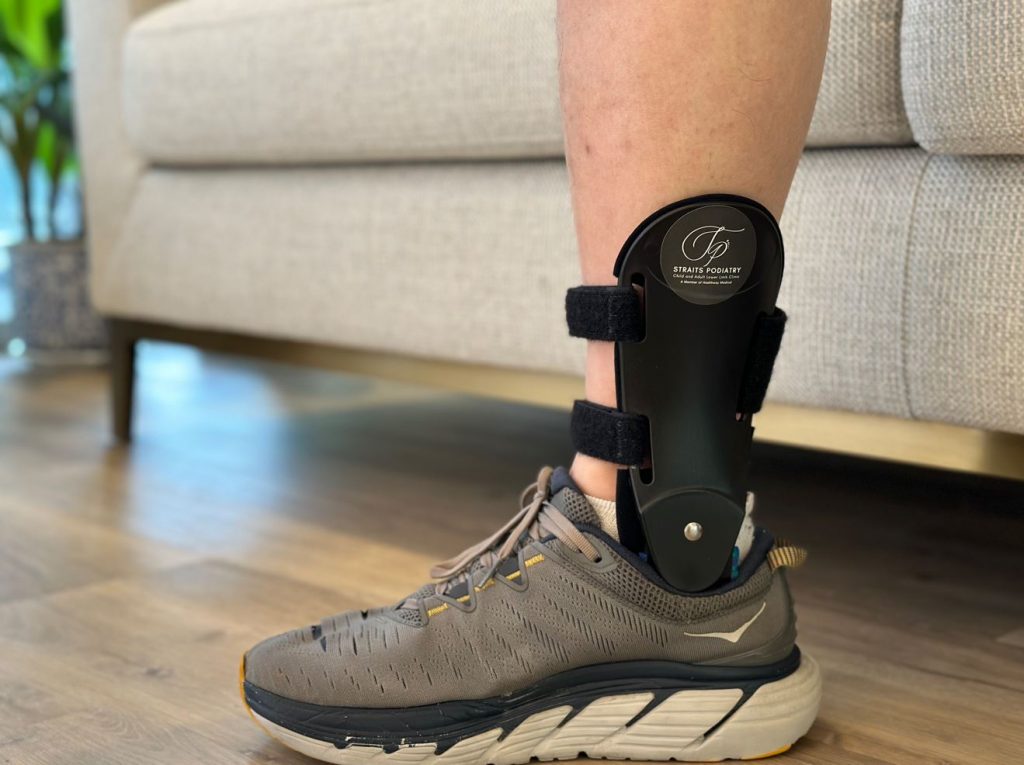
- Ankle-foot orthoses (AFO) or ankle braces can help stabilise and realign the significant flat foot deformity and offload the posterior tibial tendon.
- If the injury is beyond conservatively treatable, surgery is usually the last resort. Flatfoot correction or tendon repair are among the surgical options for treating late-stage posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Preventing Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Given how detrimental PTTD can be, your main goal should be to prevent yourself from getting it. While not every case is preventable, you can reduce your risk by:
- Wearing supportive shoes, especially if you stand or walk a lot.
- Increase your physical activity gradually and build up your training.
- Take sufficient rest and breaks.
- Stretching and strengthening the calf and ankle muscles.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the tendon.
Simple lifestyle adjustments like the ones above can make a big difference in preventing PTTD injury or in preventing recurrence after you recover.
Have Your Posterior Tibial Tendonitis Managed at Straits Podiatry
When ankle discomfort starts to hinder your daily activities, it is a sign that your leg needs help. At Straits Podiatry, we emphasise obtaining the right diagnosis and then consider all factors, including your activities, shoe selection, calf flexibility, and foot mechanics, to determine the cause of your pain.
From there, we design a management plan that fits your life. This will include footwear recommendations, custom insoles, activity guidance, and simple home exercises to ease strain. If symptoms continue to persist, we can also explore EMTT and focused ESWT as part of a comprehensive approach. Speak with our team today or book a consultation for a thorough assessment and a personalised recovery plan to get back to comfortable movement.
Frequently Asked Questions on posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Is posterior tibial tendonitis the same as flat foot?
No, it is not. Posterior tibial tendonitis is an injury caused by the inflammation of the tendon. In contrast, flat foot is a foot deformity condition. However, having a flat foot can increase the risk of posterior tibial tendinitis. Vice versa, an untreated case of posterior tibial tendon injury can also progress to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and result in a flat foot deformity. Simply put, one can lead to the other, but they are not the same condition.
How long does recovery take?
If you manage to detect the issue and start conservative treatment for posterior tibial tendonitis early, you may feel better within 4 to 8 weeks. However, advanced tendon dysfunction may take significantly longer, especially if surgery is necessary.
Can I still exercise if I have posterior tibial tendonitis?
Yes, you can. However, we recommend switching to lower-impact activities such as swimming and flat-terrain cycling to keep tendon stress low until you recover. You should also avoid an incline treadmill walk, as it puts the posterior tibial tendon under high stress despite the activity being lower-impact.
Do orthoses really help?
Yes. Orthoses are proven in research to be one of the standard non-surgical treatments because they directly reduce stress on the tendon by restoring proper foot alignment and gait pattern.
When should I see a podiatrist?
If you experience persistent ankle or arch pain, swelling, or difficulty with mobility for more than 2 weeks, it’s time to consult a podiatrist. Early intervention is critical as it prevents progression into posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.