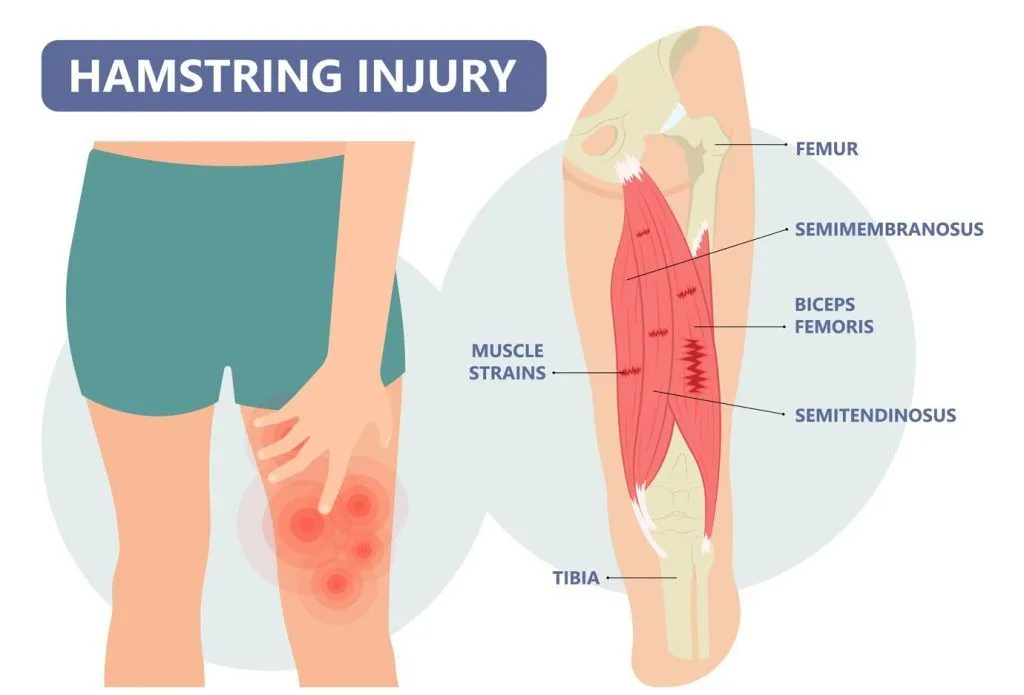
What is Hamstring Strain?
Hamstring strain is a common injury of the hamstring muscles that results in posterior thigh pain. Like calf strain, hamstring strain commonly affects individuals who participate in high-impact sports such as football or basketball and can severely affect your ability to walk or run after.
Causes of Hamstring Strain
The hamstrings muscle group is made up of 3 different posterior thigh muscles, namely biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. Hamstring strain occurs when the muscle is contracting whilst being stretched beyond its limit, causing a degree of tear in the muscle fibres.
Hamstring strain can be classified into 3 gradings:
- Grade 1 – Mild, only a small amount of muscle fibres are torn, and the patient is usually able to walk without pain, but unable to exercise.
- Grade 2 – Moderate, partially-torn muscle, typically results in acute pain and swelling and affects walking
- Grade 3 – Severe, significantly torn muscle (or full rupture), resulting in loss of strength and function
Need Help? See A Podiatrist Today
Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain
Risk factors of hamstring strain include:
- Old age
- History of a hamstring injury
- Tight hamstring muscles or hip flexors
- Sudden increase in training intensity
- Inadequate recovery
- Muscular imbalance
- Weak core stability
- Football or basketball players
- High-impact sport enthusiast
- Sprinters

Signs and Symptoms of Hamstring Strain
Signs and symptoms of hamstring strain include:
- Posterior thigh pain, affecting the ability to run or jump
- Palpable tenderness
- Swelling
- Difficulty in extending the knee
- Bruising or ecchymosis (in moderate-to-severe cases)
Hamstring Strain Treatment in Singapore
Managing hamstring strain involves addressing the injured muscle fibres and restoring the strength and function of the hamstring muscles. It is important to manage hamstring strain properly as its recurrence risk is high.
Treatment options for hamstring strain in Singapore include:
- Rest
- Ice
- Progressive strengthening and rehabilitation
- Physical therapy
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy to stimulate blood flow and the healing of the injured muscle fibres
- Radial pressure wave therapy to improve muscle flexibility